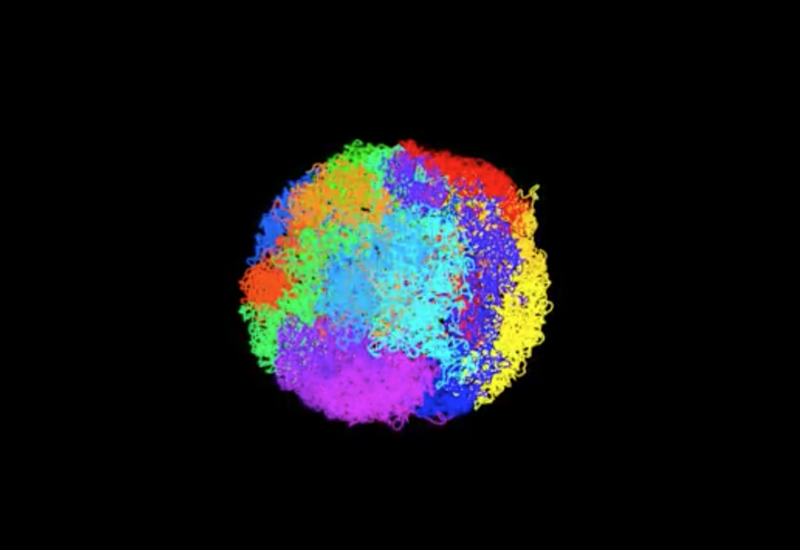
Enlarge / Intact genome from a mouse embryonic stem cell with 20 chromosomes colored differently (credit: University of Cambridge and MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology)
In a first, researchers have worked out a way to unravel and model the tangled, 3D structures of intact mammalian genomes from individual cells.
The new method, published Monday in Nature, could help researchers study how the complex loops, twists, and bunches of a tightly packaged genome influence which bits of the blueprints are actively used by the cells, and when.
In humans, for instance, genome packaging bundles nearly two meters’ worth of DNA strings into a nucleus about 0.005 millimeters wide. How all that DNA is bundled affects whether important genes are available for decoding by cellular machinery, while others are boxed up and shoved aside until they’re needed. Such carefully orchestrated genetic activity affects everything a cell does—from carrying out basic functions, to allowing stem cells to differentiate into any type of cell, to triggering diseases.

